Pallet wrapping plays a crucial role in warehouse safety and operational efficiency. Understanding and implementing pallet wrapping rules is essential for maintaining stability, protecting goods, and minimizing the risk of accidents during handling and transport. These rules provide specific guidelines on wrapping techniques and load securing practices, which are critical in both year-round and seasonal operations. In a pallet wrapping factory, adhering to these rules ensures uniformity in the wrapping process, enhancing both safety and consistency across large-scale operations. By following pallet wrapping guidelines, companies can enhance inventory protection, prevent product loss, and reduce workplace injuries associated with unsecured loads. PWP Stretch Film offers products that support these guidelines, ensuring that goods are secured effectively. Following these rules ultimately contributes to a safer, more productive warehouse environment while also improving logistics and operational consistency. Pallet wrapping rules ensure cargo stability by using the right pallet, stretch film, and uniform tension to secure products and minimize damage during transport.
Pallet wrapping rules PDF resources provide essential guidance for those handling and securing palletized loads in warehouse settings. These downloadable resources offer clear, standardized instructions that help ensure safe and consistent pallet wrapping practices across various types of operations. By using a pallet wrapping rules PDF, warehouse teams can easily access and reference critical procedures that support both safety and efficiency.

These PDFs are valuable tools for several reasons, including:
Typically, pallet wrapping rules PDFs include comprehensive guidelines covering:
Pallet wrapping rules PDF resources are indispensable tools that support safe practices and improved warehouse productivity, making them a key asset for any warehouse operation.
Ensuring safe and compliant pallet wrapping practices is a priority in any warehouse setting. Adhering to OSHA guidelines on pallet wrapping rules is critical in reducing workplace injuries, enhancing load stability, and maintaining a productive environment. OSHA’s recommendations provide detailed safety measures that address common risks associated with pallet wrapping, including ergonomic concerns and proper wrapping techniques. Incorporating these OSHA-compliant practices within the framework of pallet wrapping rules helps to create a safer workspace for employees, minimizes damage to inventory, and contributes to overall operational efficiency.
Understanding and applying OSHA’s guidelines within pallet wrapping rules can significantly improve safety. Here are some OSHA-compliant practices recommended for warehouse safety:
Adhering to OSHA’s pallet wrapping rules offers multiple benefits for workplace safety and productivity:
Here are some examples of OSHA-compliant practices included in pallet wrapping rules that support a safer, more organized workplace:
OSHA’s guidelines extend to the equipment used in pallet wrapping, whether manual or machine-based, to ensure safe handling and operation. When manually wrapping pallets with hand stretch film, OSHA recommends using lightweight, ergonomic tools that allow workers to maintain a comfortable posture, which helps prevent fatigue and injury. For operations wrapping a high volume of pallets with machine stretch film, OSHA encourages using automated or semi-automated wrapping machines, as these reduce the physical strain on workers and offer more consistent results.
For equipment usage, adhering to these OSHA-compliant practices is recommended:
OSHA guidelines emphasize load stability as a core component of pallet wrapping rules, especially in fast-paced warehouse environments. Load stability is crucial not only for protecting inventory but also for preventing accidents during transit or storage. When wrapping pallets, OSHA recommends these best practices for load stability:
By following these OSHA-compliant pallet wrapping rules, businesses can foster a safer, more organized work environment and create efficient systems for pallet handling and storage. Pallet wrapping rules rooted in OSHA guidelines help organizations meet legal standards, protect their workforce, and maintain a high standard of operational safety.
Incorporating stretch wrap machine safety within pallet wrapping rules is crucial for reducing workplace injuries and ensuring consistent, secure wrapping results. Stretch wrap machines simplify and speed up the wrapping process, making them essential for operations with a high volume of pallet handling. However, without proper safety protocols, these machines pose significant risks. By following comprehensive pallet wrapping rules, which include specific guidelines for stretch wrap machine safety, warehouses can maintain a safer environment, protect employees, and minimize inventory damage.
Stretch wrap machine safety is a vital component of pallet wrapping rules, providing clear guidelines that promote secure machine operation and reduce the risk of accidents. These rules typically address machine setup, safe distance maintenance, load positioning, and other safety measures to ensure the secure operation of the wrapping machine. Implementing these rules not only protects employees but also improves the efficiency and quality of the wrapping process.
To maintain a safe work environment, it is essential to implement best practices for operating stretch wrap machines as part of pallet wrapping rules. Key safety practices include:
Load adjustments are an essential aspect of machine safety. Adjusting load position and securing it properly ensures that the stretch wrap machine operates smoothly and that the load remains stable during transport. Guidelines on load adjustments in pallet wrapping rules contribute to both machine safety and load security.
Here are some essential load adjustment practices:
Implementing these safety guidelines as part of pallet wrapping rules offers numerous benefits:
To further illustrate how these safety guidelines work in practice, here are specific examples included in comprehensive pallet wrapping rules:
Training is crucial for ensuring employees understand how to safely operate stretch wrap machines as part of pallet wrapping rules. Training programs should cover the following:
Routine inspections are essential to maintaining the safety and efficiency of stretch wrap machines. Inspections should include the following steps:
Following these routine checks, along with the other best practices outlined above, makes stretch wrap machine safety a robust component of pallet wrapping rules. These comprehensive rules contribute to a safer, more efficient, and compliant warehouse environment, where both equipment and employees are protected.
Effective pallet wrapping rules for guarding equipment are essential in creating a safe work environment, particularly when working with machinery that involves moving parts or powerful mechanical functions. Equipment guarding not only protects employees from injury but also helps maintain a controlled and efficient warehouse setting. By following specific pallet wrapping rules that include provisions for equipment guarding, warehouses can reduce accident risks, ensure compliance with safety standards, and safeguard their workforce.

Pallet wrapping rules for equipment guarding are designed to prevent accidental contact with hazardous machine parts, such as rollers, stretch arms, and any moving components associated with pallet wrapping machines. Proper guarding serves as a barrier between the operator and potential hazards, ensuring that hands, clothing, or other materials do not get caught in the machinery during operation.
Key components of these guarding rules include:
Installing safety guards as part of pallet wrapping rules is crucial for reducing the likelihood of workplace accidents. Properly installed safety guards are effective in preventing injuries and contribute to a smoother, more productive workflow by ensuring that employees feel safe while operating or working near pallet wrapping machinery.
The advantages of including equipment guarding in pallet wrapping rules extend beyond physical safety, benefiting both operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. Some of the key benefits include:
When implementing pallet wrapping rules for guarding equipment, certain guidelines ensure both safety and compliance:
Effective guarding practices can vary depending on the type of pallet wrapping machine, but the following are some commonly applied practices:
Compliance with regulations for equipment guarding is an essential aspect of pallet wrapping rules. Adhering to these rules protects employees and helps organizations meet legal obligations, avoiding penalties and improving workplace safety.
To ensure compliance:
By integrating comprehensive pallet wrapping rules for equipment guarding, warehouses can establish a robust safety culture that prioritizes the well-being of employees and aligns with industry standards. These rules create a safer and more efficient environment where workers can operate machinery with confidence, reducing the likelihood of accidents and supporting a productive workplace.
Following pallet wrapping rules for best practices is essential to ensure load security and prevent damage during transport. Securely wrapped loads contribute to safer handling, minimize shifting risks, and protect goods from external elements. By applying these best practices, warehouses can enhance the stability of palletized goods, reduce product losses, and optimize their logistics processes.
Effective pallet wrapping rules emphasize specific techniques for load preparation, wrap application, and load stability assessments. These rules, when followed correctly, can help maintain the integrity of goods throughout transport and storage.
Proper load preparation is the first step in securing goods effectively. Pallet wrapping rules for load preparation ensure that items are stacked correctly, making the wrapping process more effective. Here are some essential practices:
Applying stretch wrap effectively is a central component of pallet wrapping rules for load security. Proper wrap application ensures that the load remains stable throughout transport. Here are best practices for applying stretch wrap:
Pallet wrapping rules recommend assessing the load’s stability after wrapping to ensure it is secure for transport. A final load assessment can help identify any issues that could lead to shifting or breakage. Best practices in load assessment include:
Adhering to pallet wrapping rules for load security offers several benefits that enhance operational efficiency and minimize risks:
Here are examples that illustrate how pallet wrapping rules improve load security in practical situations:
To achieve optimal load security, additional steps can be incorporated into the pallet wrapping process:
By following these pallet wrapping rules for load security, warehouses and distribution centers can improve the safety and efficiency of their operations. Proper load preparation, effective wrap application, and thorough load assessments ensure that palletized goods remain secure from the warehouse to their final destination. These best practices provide a practical approach to load security, minimizing product loss, enhancing worker safety, and supporting overall operational productivity.
In the world of logistics and warehousing, pallet wrapping plays a crucial role in ensuring the stability, protection, and transportability of goods. Among the various factors influencing effective pallet wrapping, containment force is one of the most critical. Containment force refers to the amount of pressure exerted by the stretch film to keep the load stable and secure, preventing shifting, tilting, or collapsing during handling and transportation. Without proper containment force, wrapped pallets may become unstable, leading to product damage, transportation hazards, and increased costs.
However, achieving the right containment force is not just about wrapping a pallet tightly—it depends on multiple interrelated factors. The type of stretch film, its thickness, elasticity, and the wrapping technique all contribute to determining the final containment force applied to the load. Additionally, different types of pallet loads require different levels of containment force, making it essential to match the correct stretch film with the specific load requirements.
This guide will explore the key aspects of selecting stretch film correctly, including the fundamentals of containment force, the various types of stretch films available, the importance of film thickness, best practices in wrapping techniques, and cost-effective, environmentally friendly wrapping strategies. By understanding and applying these principles, businesses can improve pallet security, reduce material waste, and enhance operational efficiency.
Before selecting the appropriate stretch film, it is crucial to understand what containment force is and why it matters. Containment force is a measure of how well the film holds the load together by applying consistent tension across its surface. It is a combination of the number of film layers, the tension applied during wrapping, and the stretchability of the film.
To achieve proper containment force, the following aspects must be carefully controlled:
By understanding these factors, businesses can select the correct stretch film and adjust wrapping techniques accordingly to achieve the necessary containment force for safe and efficient transport.
Different stretch films offer varying levels of strength, elasticity, and containment force. Selecting the right type depends on the specific application, load characteristics, and environmental conditions.
Cast Stretch Film
Made using a cast extrusion process, offering superior clarity.
Blown Stretch Film
Produced through a blown extrusion process, creating a stronger film with higher puncture resistance.
Pre-Stretched Film
Mechanically stretched before being wound onto the roll, requiring less force during application.
High-Performance Film
Designed with advanced polymer technology to provide superior strength at thinner gauges.
By selecting the right stretch film type, businesses can optimize containment force while minimizing costs and environmental impact.
The thickness of the stretch film, measured in gauge, determines its strength and containment force. Using the wrong thickness can lead to inadequate load security or excessive material use.
| Gauge | Recommended Load Type | Weight Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| 60-70 | Light loads (e.g., paper products, empty containers) | Up to 1,500 lbs |
| 80 | Standard general-use applications | 1,500-2,500 lbs |
| 90-100 | Medium to heavy loads (e.g., food and beverage, construction) | 2,500-3,500 lbs |
| 115+ | Very heavy or irregular loads (e.g., metal parts, machinery) | Over 3,500 lbs |
Choosing the correct gauge ensures that the film provides enough containment force without unnecessary material waste.
Even the best stretch film will not perform effectively if applied incorrectly. Proper wrapping techniques help achieve uniform containment force, reduce film waste, and enhance load security.
Following these techniques ensures that the correct containment force is applied without excessive film use, optimizing both security and efficiency.
With increasing focus on sustainability, businesses must balance cost efficiency with environmental responsibility when selecting stretch film.
By making informed choices, companies can reduce costs, minimize environmental impact, and improve operational efficiency.
Selecting the right stretch film and achieving proper containment force is essential for pallet stability, load protection, and cost efficiency. By understanding containment force, choosing the correct film type and thickness, implementing effective wrapping techniques, and considering environmental impact, businesses can enhance pallet wrapping performance while minimizing waste. Proper pallet wrapping ensures safer transportation, reduced product damage, and optimized supply chain operations, making it a critical aspect of modern logistics.
Pallet wrapping is an essential practice for securing cargo and preventing damage during transport. Properly wrapping boxes on pallets helps ensure the stability and safety of the load. It prevents shifting, protects goods from external elements, and minimizes the risk of damage. To achieve effective stretch wrapping, it’s crucial to follow a series of steps that involve selecting the right materials, securing the load with proper tension, and ensuring uniform coverage. This section will explore the detailed steps and considerations that go into correctly stretch wrapping boxes on pallets.
Before you begin the wrapping process, it’s essential to choose the right materials to ensure a secure and stable load. The most common material used for stretch wrapping is polyethylene stretch film. This film comes in various gauges and types, so selecting the right one is crucial based on the size, weight, and type of products being wrapped. You should use a high-quality stretch film that offers enough strength to hold the boxes securely, without compromising the integrity of the load. Additionally, you may want to choose a film that is designed for your specific application, such as weather-resistant or anti-static film if the cargo is sensitive.
Properly preparing the pallet and products before wrapping is crucial for achieving optimal results. Begin by ensuring that the boxes are stacked correctly on the pallet. The boxes should be arranged with even weight distribution to avoid tipping during transport. Additionally, ensure that there are no protruding edges or gaps between the boxes that might cause instability. If necessary, use corner protectors or edge boards to reinforce the load and prevent the film from damaging the corners of the boxes. Once the pallet is correctly stacked and reinforced, it’s ready for the wrapping process.
When beginning the stretch wrapping process, ensure that the stretch film is securely attached to the pallet. Start by anchoring the film at the base of the pallet, wrapping the bottom 30-50% of the pallet and the bottom layer of boxes. This provides a solid foundation for the rest of the wrap. Pull the film tightly around the pallet while maintaining consistent tension to ensure the film is evenly distributed. Avoid applying too much tension initially, as this can cause the film to snap. The goal is to create a strong foundation that holds the boxes in place while allowing for a bit of stretch in the film to enhance the load’s stability.
As you work your way up the pallet, continue wrapping each layer of boxes with the stretch film, ensuring that each new wrap overlaps the previous layer by 50%. This overlap is crucial for holding the load firmly and preventing shifting during transport. Keep the film taut as you move upward, maintaining consistent tension across all layers. It’s important to wrap at least 3-4 layers of film around the pallet to ensure maximum load stability, especially for heavier or more delicate items. Adjust the tension as needed to prevent the film from becoming too loose, which could lead to instability.
Once you’ve wrapped the pallet to the desired height, focus on securing the top layers to lock the load in place. At the top of the pallet, wrap the stretch film around the top layer of boxes and the top edge of the pallet, ensuring that the film holds the load securely. You may want to add an additional layer or two around the top to create a reinforced seal. To finish, cut the stretch film and tape or secure the end of the film to prevent it from unraveling. If the pallet is particularly heavy or the boxes are fragile, consider adding extra layers of film to ensure additional security.
After the pallet has been wrapped, inspect the load to ensure it is stable and secure. The stretch film should be taut and evenly applied around the entire pallet. Check that there are no loose areas or gaps in the wrapping, as these could lead to shifting or damage during transport. The pallet should feel solid and firm, with no noticeable wobble or instability. If necessary, reapply more film to areas that feel loose or unsecure.
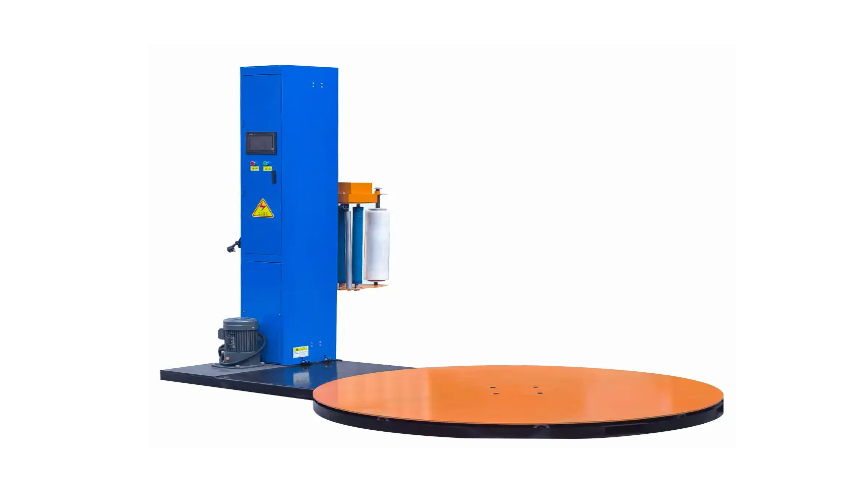
To further enhance the wrapping process, many companies use automated stretch wrapping machines that ensure uniform tension and coverage. These machines can adjust film tension, wrap speed, and layering to ensure consistency and high-quality wraps every time. For large-scale operations or high-volume shipments, incorporating this technology can improve efficiency and reduce human error. Automated systems can also apply additional features such as pre-stretching the film, which uses less material while maintaining strength, offering cost efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
By following these detailed steps and ensuring that each layer is applied carefully and securely, you can achieve a properly wrapped pallet that ensures the safety and stability of your products during transport. Pallet wrapping rules not only enhance product protection but also optimize handling, minimize loss, and improve overall efficiency in logistics operations.
When it comes to pallet wrapping, the use of stretch film is crucial for securing goods and ensuring stability during transport. However, whether you’re wrapping manually or using a machine, the approach and techniques vary significantly. While both methods serve the same purpose—to stabilize and protect the load—the rules for applying stretch film differ based on the equipment used and the volume of wrapping required. This section explores the differences between manual and machine use of stretch film, focusing on key aspects such as efficiency, consistency, tension control, and material usage.
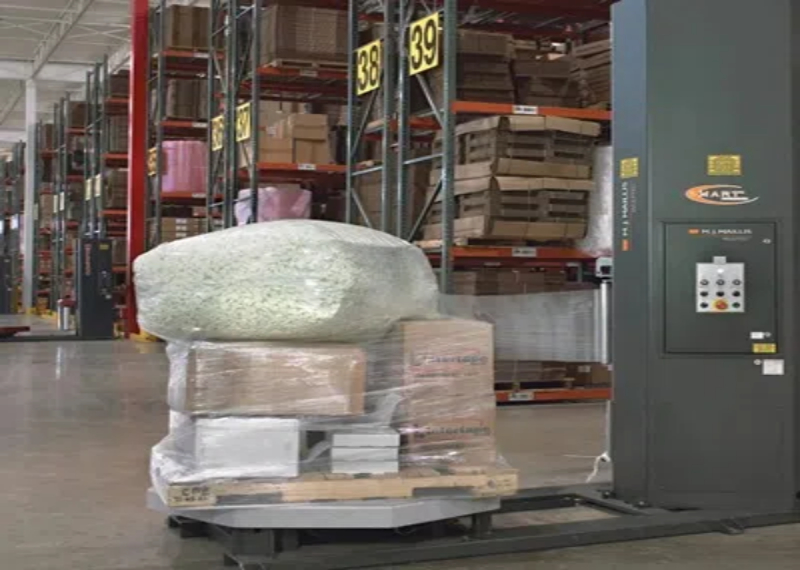

The primary difference between manual and machine wrapping is the speed and efficiency with which the task is completed. Manual wrapping is typically slower, as it relies on human labor to wrap the film around the pallet. The operator must adjust the film, tension, and overlap as they wrap, which can be time-consuming, especially for larger pallets or high-volume operations.
In contrast, machine wrapping uses automated equipment that wraps pallets at a much faster rate, often with greater consistency and less manual effort. Automated stretch wrappers are designed to quickly rotate the pallet while applying the stretch film with precise tension and overlap. This allows for high-speed wrapping, making it ideal for large warehouses or production lines where many pallets need to be wrapped each day. The efficiency of machine wrapping can significantly reduce labor costs and improve overall throughput.
Consistency in applying stretch film is another important factor where manual and machine wrapping differ. In manual wrapping, the operator must maintain even tension and ensure consistent overlap as they move around the pallet. While experienced operators can achieve a good result, it can be challenging to maintain uniformity with each pallet. Inconsistent tension can lead to weak spots, causing the load to shift or potentially become unstable during transport.
Machine wrapping, on the other hand, offers superior consistency. The machine ensures even tension throughout the wrap, preventing slack or excessive tightness in the film. Additionally, the machine applies a consistent number of layers, ensuring a uniform wrap across all pallets. This uniformity is crucial for maintaining load stability and reducing the risk of damage during shipping and handling.
Tension control is a key element in pallet wrapping that can significantly affect the stability of the load. In manual wrapping, the operator must control the tension of the stretch film by pulling it with their hands. This can lead to varying tension levels, depending on the skill and experience of the operator. If too much tension is applied, the film can tear, or the load could become deformed. If too little tension is applied, the wrap may not secure the load adequately, leading to instability during transport.
With machine wrapping, tension control is much more precise. Automated stretch wrappers typically feature built-in mechanisms that allow the machine to stretch the film to a set percentage before applying it to the pallet. This ensures that the film is consistently stretched to the optimal tension level, providing maximum holding power without risking damage to the load. The ability to control tension automatically is one of the key advantages of machine wrapping.
The amount of stretch film used during pallet wrapping is also a significant factor, especially when considering cost-effectiveness and waste reduction. In manual wrapping, there is a tendency to use more material than necessary, as it’s difficult for operators to gauge the correct amount of film needed to secure the load. Over-wrapping can lead to excess material usage and higher costs. Additionally, in some cases, manual operators may apply film unevenly, which could result in more material being used in certain areas than others.
Machine wrapping, particularly when using pre-stretch technology, can significantly reduce material waste. Pre-stretching the film before application ensures that the film is stretched to its maximum capacity, using less material while still providing the same level of load security. This results in less waste, reduced costs, and more efficient use of stretch film. Automated systems can also optimize the amount of film used per pallet, further minimizing material waste.
Manual wrapping offers more flexibility when it comes to handling irregularly shaped or non-standard pallets. Operators can adjust their technique to accommodate different shapes and sizes, making it easier to wrap unique or awkwardly sized loads. This flexibility is especially important for smaller businesses or operations where the size of pallets may vary frequently.
Machine wrapping, while faster and more consistent, is typically less adaptable to irregular loads. Most stretch wrappers are designed to handle standard pallet sizes and shapes. For non-standard pallets, adjustments may need to be made to the machine setup, or the load may need to be manually adjusted before wrapping. While machines can often accommodate different pallet sizes, it can require additional time and effort to adjust the settings for varying load types.
The cost of using manual vs. machine wrapping systems is a key consideration for many businesses. Manual wrapping is relatively inexpensive because it doesn’t require significant upfront investment in equipment. The primary costs are labor and stretch film. However, as operations scale up or if high volumes of pallets need to be wrapped daily, labor costs can increase significantly.
Machine wrapping, while initially more expensive due to the cost of the wrapping equipment, can offer long-term cost savings through increased speed, reduced labor costs, and minimized stretch film waste. For high-volume operations, the investment in a machine may quickly pay for itself. Moreover, machine wrapping systems often offer advanced features like film pre-stretching, further enhancing cost-efficiency.
While the core purpose of pallet wrapping remains the same—securing and stabilizing loads for safe transport—manual and machine wrapping have distinct differences in terms of speed, consistency, material usage, and cost-effectiveness. Manual wrapping offers flexibility and is cost-effective for small operations or irregular loads, but it can be time-consuming and prone to inconsistencies. On the other hand, machine wrapping provides higher efficiency, greater consistency, and material savings, making it ideal for high-volume operations. Understanding the differences between these methods and the corresponding pallet wrapping rules can help businesses choose the best approach based on their specific needs and operational requirements.
Using stretch film to wrap pallets is a common practice in warehouses to ensure that goods are securely packaged and protected during transport. However, this process can pose several safety hazards to warehouse workers if not handled correctly. Understanding the safety risks associated with stretch film and adhering to established pallet wrapping rules can help mitigate these dangers and create a safer working environment. This section will explore the potential safety hazards involved in using stretch film for pallet packaging and outline strategies for minimizing these risks through proper safety measures and adherence to pallet wrapping rules.
One of the most common safety hazards in warehouses when using stretch film for pallet packaging is the risk of slips, trips, and falls. As stretch film is unwound and applied to pallets, the film can sometimes fall to the floor, creating tripping hazards for workers. In busy warehouse environments, film can also accumulate in walkways or aisles, leading to accidents.
To minimize this risk, workers should be trained to handle stretch film properly and dispose of any excess film immediately. Pallet wrapping rules require that film is kept neatly and that the work area is regularly cleared of any stray film or debris. Additionally, it is important to use equipment like film dispensers to control the film and prevent it from touching the floor. Keeping work areas well-lit and maintaining clear pathways can further reduce the likelihood of falls.
Stretch film can be sharp when cut, and workers may inadvertently injure themselves while using knives or other tools to trim the film. Cuts or puncture wounds are common injuries associated with this process, especially when workers are handling the film in a rush or without proper safety equipment.
To reduce the risk of cuts and punctures, workers should be provided with proper safety gloves, and knives should be fitted with safety features such as retractable blades. It’s essential to train workers on safe handling and cutting techniques, ensuring they are aware of the potential hazards when using sharp tools. Following pallet wrapping rules also includes having a dedicated area for film cutting, equipped with safety tools, to minimize unnecessary movement and distractions during the wrapping process.
Manual pallet wrapping can put a strain on workers’ muscles, particularly their shoulders, arms, and wrists, if the task is performed repeatedly over long periods. Repetitive motion and the pressure required to apply stretch film can lead to musculoskeletal injuries, including sprains, strains, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
To prevent RSIs, employers should ensure workers take regular breaks, especially during long wrapping sessions. In addition, ergonomic training can be provided to help employees use their bodies more efficiently while wrapping. Workers should also be encouraged to vary their tasks throughout the day to reduce the chances of developing repetitive strain. Using automated or machine wrapping systems, when possible, can also alleviate the physical strain on workers and allow for more efficient packaging.
Another potential danger of using stretch film is the risk of entanglement. Stretch film is strong, but it is also flexible and can wrap around workers’ hands, arms, or other body parts if not handled properly. This can lead to serious injuries or even cause workers to become stuck or trapped. This hazard is particularly prevalent when using manual wrapping methods that involve pulling and twisting the film by hand.
To minimize the risk of entanglement, pallet wrapping rules dictate that workers should be trained to keep their hands and clothing away from the stretch film as it is being applied. Using automatic or semi-automatic machines to apply stretch film can reduce the chances of entanglement, as these machines are designed to handle the film without direct worker involvement. Additionally, workers should be provided with personal protective equipment (PPE) to reduce the risk of getting caught in the film.
In some cases, workers may need to manually lift or move heavy pallets to wrap them with stretch film. Lifting heavy loads improperly can lead to back injuries, strains, or muscle tears, especially if the pallet is not properly balanced or if it is difficult to maneuver. The weight of the pallet, combined with the effort required to wrap it, can contribute to overexertion.
Pallet wrapping rules emphasize proper lifting techniques to avoid injuries. Workers should be trained in the correct posture for lifting and moving heavy pallets, including the use of mechanical aids like forklifts or pallet jacks when necessary. Lifting aids can help avoid strain and ensure workers are not overexerting themselves. Additionally, for particularly heavy loads, a team approach may be required to share the physical effort.
In certain environments, stretch films may contain chemicals that could pose health risks if inhaled or exposed to skin over prolonged periods. Some stretch films, particularly those used in food packaging, may have additional additives or coatings, and while most stretch films are safe, improper storage or handling can lead to accidental exposure.
To avoid exposure to harmful chemicals or fumes, it is important to follow safety data sheets (SDS) provided by the stretch film manufacturer. These documents offer detailed information on any potential hazards associated with the film. Pallet wrapping rules include proper storage of film materials in well-ventilated areas, away from heat sources, and regular inspection for signs of deterioration or degradation. Workers should also be provided with PPE, such as gloves and masks, if necessary, when handling specific types of film.
Excess stretch film waste can create environmental hazards, especially in a warehouse setting where large volumes of pallets are wrapped. Discarded stretch film may contribute to plastic pollution if not disposed of properly. Moreover, excessive use of stretch film can lead to higher costs and waste.
Pallet wrapping rules promote waste reduction by encouraging proper disposal methods for used film and utilizing eco-friendly film options where possible. Workers should be instructed to always dispose of stretch film responsibly in designated recycling bins to prevent environmental contamination. Additionally, some businesses implement systems for reusing stretch film or switching to more sustainable alternatives, reducing both waste and environmental impact.
While stretch film plays a crucial role in securing pallets and protecting goods during transport, its use in warehouses can present a range of safety hazards. By understanding these risks and implementing proper pallet wrapping rules, warehouse managers can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents and injuries. From preventing slips and falls to minimizing repetitive strain and entanglement, clear safety protocols and employee training are essential. Moreover, the use of automated wrapping systems can further enhance safety by reducing human error and physical strain. By applying these safety measures and adhering to best practices, businesses can maintain a safe and efficient working environment while ensuring the secure packaging of pallets.
OSHA, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, has specific guidelines to ensure safe handling, stacking, and storage of pallets in the workplace. These rules are designed to prevent injuries and improve overall warehouse safety. Key points include ensuring that pallets are in good condition before use, with no visible signs of damage, as broken or unstable pallets can lead to collapses or accidents. OSHA also emphasizes proper stacking techniques, such as aligning pallets evenly and keeping sharp edges or corners away from aisles to avoid contact injuries.
Additionally, there are height and weight limitations. OSHA recommends stacking pallets no higher than 15 feet and maintaining a weight load that doesn’t exceed the pallet’s rated capacity. Another important factor is placement – OSHA advises against placing stacked pallets in high-traffic areas to avoid potential hazards. Lastly, all workers should receive proper training on handling and storing pallets safely, including techniques for lifting and stacking to reduce the risk of musculoskeletal injuries. Following these OSHA rules helps ensure a safer, more efficient workplace.
The number of times a pallet should be wrapped depends on factors like the type of load, its stability, and the purpose of wrapping. Generally, for hand-wrapped pallets, wrapping around the base 4-5 times provides a solid foundation, securing the load to the pallet and reducing movement. Moving up the pallet, each layer should overlap the previous one by 50% for added stability. For machine-wrapped pallets, typically 3-4 times around the base is sufficient, with additional layers depending on the load’s height and weight.
Heavy or irregularly shaped loads might require more layers, especially around corners and the top of the pallet, to prevent shifting during transport. Consistent tension throughout the wrapping process is also essential to avoid loose wrapping, which could compromise stability. If using a pre-stretch film, like PWP Stretch Film, fewer layers might be needed due to its strong elastic memory, which maintains a tight hold. In general, evaluating the load’s size, weight, and shape will help determine the optimal number of wraps for secure transport.
The correct way to wrap a pallet involves several key steps. First, ensure the cargo is stacked properly with uniform height and space between layers to prevent shifting. Use a high-quality stretch film, ensuring that it has the appropriate tension for secure wrapping. Start wrapping from the bottom of the pallet, securing the stretch film around the bottom 30-50% of the pallet. As you wrap, maintain uniform tension on the film to avoid slack and ensure it is evenly distributed. Wrap upwards, overlapping each layer by at least 50% of the previous wrap to ensure complete coverage. Finish the wrap at the top, securing the film tightly to prevent any movement. Proper wrapping also involves securing the pallet by taping the film at the top and bottom to keep the load intact during transportation.
Safety guidelines for pallets focus on proper handling, storage, and usage to avoid accidents and damage. Always inspect pallets for damage, such as broken slats, protruding nails, or sharp edges. Damaged pallets should be removed from use immediately to avoid injury or cargo damage. When stacking pallets, ensure they are stable and evenly distributed. The weight should be centered to prevent tipping. Pallets should be stored in a clean, dry area, free from environmental hazards like moisture or pests that could cause deterioration. When handling pallets manually, wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves, to avoid injury from splinters or sharp objects. Ensure that forklifts or pallet jacks are operated by trained personnel, and always follow safe lifting techniques. Pallets should also be wrapped securely to avoid shifting during transport, reducing the risk of accidents.
The code for wooden pallets often refers to the ISPM 15 (International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures) standard, which requires the treatment of wood packaging materials to prevent the spread of pests. The standard includes a heat treatment (HT) or fumigation (MB) process to kill any insects or pathogens in the wood. After treatment, pallets are marked with a stamp showing compliance, typically featuring the country of origin, the treatment method (HT or MB), and the issuing authority. This ensures the pallet complies with international shipping regulations and reduces the risk of pests being transferred between countries. The treatment code, along with other labeling information, helps customs officials verify that the pallet meets the standards necessary for global trade.
Pallet requirements in a warehouse focus on ensuring the safe, efficient storage, and movement of goods. Pallets must be sturdy, free from damage, and sized appropriately for the products they carry. They should be able to support the weight of the load without bending, breaking, or shifting. In warehouses, pallets should be stacked in a way that maintains accessibility while maximizing storage space. It’s crucial to ensure that all pallets are compliant with safety standards, such as ISPM 15, to prevent the introduction of pests. Proper labeling and tracking of pallets help with inventory control. Pallet racking systems should be compatible with the types of pallets being used, ensuring that they can support the weight and dimensions of the loads. It’s also essential to ensure that pallets are wrapped properly to secure goods and prevent shifting during handling.
The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) has specific requirements for pallets used in the food industry to prevent contamination and ensure safe storage and transportation of food products. Wooden pallets are subject to the ISPM 15 standard to prevent the spread of pests, while pallets used for food must be kept clean and free from chemicals, dirt, and debris that could contaminate food products. Pallets should be made of materials that do not retain moisture or harbor bacteria. They must be regularly cleaned and sanitized if they are reused. Additionally, pallets must be stacked and stored in a manner that prevents contact with the floor, and they must be wrapped securely to avoid contamination from external sources during transport. Pallet design and handling should minimize the risk of cross-contamination, ensuring food safety from storage to transportation.
The industry standard for pallets varies by sector but typically follows guidelines for size, weight, and strength. The most common pallet size is the 48” x 40” (1219 mm x 1016 mm) GMA (Grocery Manufacturers Association) pallet, used widely in North America. Pallets must be able to support a typical load, often around 2,000 to 3,000 pounds, depending on the material and design. Industry standards also include safety regulations, such as the ISPM 15 for international shipping, and specifications for pallet durability, such as the use of hardwood or plastic materials. In the context of warehouse and logistics operations, pallets must be sturdy, stable, and easy to handle by forklifts and pallet jacks. Pallet wrapping rules are also integral, ensuring that products are securely wrapped for transport and storage to minimize damage and ensure safety.
The maximum height for packing a pallet is determined by a combination of safety standards, load capacity, and handling equipment. Typically, the height of a pallet load should not exceed 5 to 6 feet (1.5 to 1.8 meters) to ensure stability and prevent tipping. The weight distribution should be even, with the center of gravity kept low to avoid imbalance. When stacking goods on a pallet, the load should be evenly distributed and stacked in a compact manner to prevent shifting. Pallets packed too high may cause instability, leading to potential accidents during transport or storage. Additionally, warehouse racking systems often have height restrictions, so it’s important to consider the overall clearance and handling capabilities when determining the height of the pallet load.
The NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) standards for pallets primarily focus on fire safety and material handling in industrial settings. Pallets made of flammable materials, such as wood, need to be stored and handled in a way that minimizes the risk of fire. The NFPA standards for pallet storage address fire protection measures, including sprinkler systems, fire-resistant coatings, and safe distance requirements between stacked pallets. These standards also emphasize maintaining clear access for fire departments and ensuring proper storage arrangements to prevent pallet pile-ups or congestion. In warehouses, the NFPA guidelines suggest maintaining proper ventilation and avoiding the storage of highly flammable materials near pallets. It is essential that warehouses follow NFPA safety guidelines to reduce the risk of fire hazards and protect both goods and personnel.
Pallet strapping involves using plastic or steel bands to secure the load on a pallet, ensuring stability during transport. The strapping method begins by placing the load on a flat pallet and wrapping the banding material around the load horizontally and vertically. The bands are tightened using a strapping tool, which helps to compress the load and hold it firmly in place. The strapping bands should be tensioned enough to secure the load but not too tight to damage the products. The ends of the straps are usually sealed with a metal buckle or welded together to keep them in place. The strapping method is commonly used in conjunction with pallet wrapping to provide additional security, especially when heavier or fragile goods are involved. Proper strapping ensures that the load remains intact and safe during handling and transport.
Pallets can be wrapped while in racking, but there are considerations to ensure safety and efficiency. Wrapping pallets in racking helps secure the load, but it’s crucial to ensure that the wrapping is done with uniform tension to prevent the load from shifting or becoming unbalanced. The process involves wrapping the stretch film around the pallet, with enough tension to ensure it holds the load securely, while avoiding excessive tightness that could deform or damage products. Pallets stored in racking should also be properly labeled and identified to minimize errors when handling or retrieving them. Additionally, it is essential to ensure that racking systems are sturdy and compatible with the size and weight of the pallets being stored. When pallets are wrapped in racking, handling should be done carefully to avoid any damage to the goods or the wrapping itself.
Pallet storage guidelines focus on ensuring the safe, efficient, and organized storage of pallets to avoid damage and improve accessibility. First, pallets should be stored on flat, dry surfaces to prevent warping or degradation of the material, especially if wooden pallets are used. It’s crucial to store pallets in a clean, organized manner with clear aisles for easy access and handling. When stacking pallets, make sure they are aligned properly, with even weight distribution, and stored at appropriate heights to avoid toppling. If pallets are used for food or sensitive goods, consider temperature and humidity controls. Additionally, ensure that pallets are inspected regularly for damage, and remove any defective pallets from use immediately. Proper labeling and tracking systems can help maintain inventory control, especially in large warehouses.
Outdoor pallet storage requires additional precautions to protect pallets from weather, pests, and other environmental factors. Wooden pallets should not be stored directly on the ground to avoid moisture absorption, which can cause degradation or mold growth. Instead, they should be placed on elevated platforms or racks to promote airflow and prevent contact with soil. In areas with harsh weather conditions, pallets should be covered with tarps or protective materials to shield them from rain, snow, or UV exposure. If possible, store pallets in shaded or sheltered areas to reduce exposure to sunlight, which can weaken the material. Regular inspections are crucial to check for wear or pest infestations. Outdoor storage should be organized to ensure easy access, and fire safety measures must be followed, especially if combustible materials are stored nearby.
When storing pallets near a building, it is essential to comply with local fire safety and building regulations. Typically, pallets should be stored at least 10 feet (3 meters) away from the exterior of a building to allow for proper air circulation, access, and fire safety measures. This distance can vary based on the material of the pallets (wooden pallets may require more space) and the type of building or facility. Additionally, it is important to avoid stacking pallets directly against the building’s walls to prevent damage to the structure and to ensure there are no blockages of emergency exits or ventilation openings. Fire codes also often dictate safe distances from building entrances and windows, so always verify local codes and regulations to ensure compliance.
The CSI (Construction Specifications Institute) code for pallet racking typically falls under Division 10 – Specialties or Division 11 – Equipment, depending on the structure of the facility. Specifically, pallet racking systems would be categorized under the code for “Storage Racks” or “Warehouse Equipment.” A more specific CSI classification could include the number “10560” or similar, which refers to shelving, storage racks, and related warehouse storage systems. For detailed and accurate classification, it is best to consult the most current version of the CSI MasterFormat or refer to manufacturer guidelines when selecting pallet racking systems to ensure compliance with construction and safety standards.
The codes on pallets often refer to standards or certifications that ensure they meet industry regulations. One common code is the ISPM 15 (International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures) stamp, which is used for wooden pallets to show that they have been treated to prevent the spread of pests. The code includes symbols indicating the country of origin, treatment method (such as heat treatment (HT) or methyl bromide (MB) fumigation), and the agency responsible for certification. Additionally, pallets may feature manufacturer-specific identification codes, serial numbers, or QR codes for tracking purposes. In some cases, color coding is used to differentiate between types of pallets or specific uses within warehouses or supply chains.
Pallet requirements focus on ensuring the pallet is structurally sound, suitable for the intended load, and compliant with safety standards. Pallets must be made of durable materials, such as wood, plastic, or metal, depending on the application. They should be capable of supporting the weight of the products being stored or transported, with the weight evenly distributed to avoid tipping. The dimensions of the pallet must be appropriate for the items, with common sizes such as the 48” x 40” GMA pallet being widely used. Pallets must be free from defects, such as broken slats or protruding nails, to prevent injury and product damage. For international shipping, pallets must meet ISPM 15 standards for pest control and treatment. Additionally, the design should allow for easy handling by forklifts or pallet jacks.
Before stacking pallets on top of each other, several important rules should be followed to ensure safety and stability. First, ensure that the pallets are structurally sound and free from damage, such as cracks, splits, or broken slats. The load on each pallet must be evenly distributed to prevent it from toppling. When stacking pallets, make sure they are aligned properly, with each pallet directly on top of the one below it, avoiding any overhang. It’s important to stack pallets with a maximum height that does not exceed safe limits, typically 5 to 6 feet (1.5 to 1.8 meters), to maintain stability. Additionally, make sure the bottom pallet is placed on a flat, level surface to avoid tipping. If the pallets are not secured with stretch film or strapping, consider securing them to prevent shifting or collapse.
Yes, blue pallets are allowed, and they are often used in specific industries or supply chains. In fact, some companies use blue pallets to distinguish their pallets from others, often for reasons related to branding, ownership, or logistics. For example, blue plastic pallets are common in the food and beverage industry because they are easy to clean, resistant to contamination, and durable. Blue pallets may also be part of a pooling system, where pallets are rented and reused by various companies within a specific network. While blue pallets are widely accepted, it’s important to ensure that they meet industry standards for strength, durability, and safety, such as the ISPM 15 certification for wooden pallets if they are being used for international shipping. Additionally, blue pallets should not be mixed with other pallet types unless they are part of an established and compatible pooling system.
Packing a pallet correctly is essential for ensuring stability, preventing product damage, and optimizing storage and transport. First, use a high-quality pallet that is free from damage. Stack the heaviest and sturdiest items at the bottom, keeping the load evenly distributed to prevent tipping. Align boxes properly, avoiding overhang, which can lead to instability. Utilize interlocking stacking methods when possible to improve structural integrity. Secure loose items with corner boards or straps before wrapping. If wrapping is used, start at the base, ensuring the stretch wrap extends below the bottom layer for anchoring. Stretch wrap should be applied with sufficient tension to keep the load from shifting while avoiding excessive pressure that could crush boxes. To finish, add a top layer of wrap or a plastic sheet to protect against dust and moisture. Label the pallet for easy identification and compliance with shipping regulations.
While stretch wrap is the most common method for securing pallet loads, several alternatives exist that offer varying benefits in cost, efficiency, and environmental impact. Strapping (or banding) is a strong option, using plastic or steel bands to tightly secure loads, especially for heavy or irregularly shaped items. Reusable pallet bands, made of durable rubber or elastic material, provide a more eco-friendly solution. Pallet netting is another alternative that offers breathability while keeping loads secure, making it ideal for transporting perishable goods. Shrink hooding, a heat-shrinkable plastic cover, offers superior protection against moisture and tampering. Adhesive pallet stabilization solutions, such as anti-slip sheets or pallet glue, help reduce movement between stacked items without additional wrapping materials. Depending on the shipping requirements, a combination of these alternatives may be used to improve efficiency and sustainability in packaging operations.
Wrapping the top of a pallet is crucial for protecting the goods from dust, moisture, and external contaminants. To do this properly, place a plastic top sheet or pallet cover over the load before applying the final layers of stretch wrap. If using manual wrapping, extend the stretch wrap above the highest point of the pallet and fold it over the top to create a protective layer. Continue wrapping around the sides, ensuring that the top is fully covered while maintaining tension. For automated wrapping machines, many models include a top sheet dispenser that applies a plastic film before completing the wrap cycle. Ensure that the wrap or cover is secure but not overly tight, which could damage the top layer of products. If additional protection is needed, consider using reinforced wrapping techniques or strapping in combination with wrap to hold the top sheet in place.
Wrapping a skid follows similar principles to pallet wrapping but may require additional considerations depending on the load type. Begin by anchoring the stretch wrap to the skid itself, looping it underneath the first layer for a strong hold. Apply the wrap around the base several times to secure the foundation before moving upward in overlapping layers. Maintain consistent tension to prevent shifting while avoiding excessive tightness that could cause damage. If the load has irregular shapes, corner protectors or edge reinforcements may be needed. Once the top is reached, wrap downward again to ensure full coverage and stability. For added security, consider using reinforced stretch film or banding in conjunction with wrapping. Finally, check for gaps or loose areas and apply additional wrap as necessary. If the skid is being stored for an extended period, a pallet cover can provide extra protection against dust and environmental factors.
Wrapping pallets can be physically demanding but is not necessarily difficult when the correct techniques and tools are used. Manual wrapping requires bending, stretching, and applying force to create tension, which can be strenuous over time. Using a wrapping turntable or semi-automatic stretch wrapper can significantly reduce labor and improve consistency. The main challenges include ensuring even tension, proper overlap, and adequate bottom anchoring to prevent shifting during transport. Inexperienced workers may struggle with achieving uniform coverage, leading to unstable loads or excessive material use. Training and proper ergonomics can make the process easier and more efficient. Additionally, selecting the right stretch film—whether hand wrap, machine wrap, or reinforced film—can impact ease of application. While wrapping pallets may require practice, following best practices and using the right equipment can streamline the process and enhance load security.
Pallet wrap, also known as stretch film, secures and stabilizes palletized loads by applying tension that holds the items tightly together. Made from linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), the film has elastic properties that allow it to stretch and contract around objects, creating a secure bond. The process starts by anchoring the wrap at the base of the pallet and applying multiple overlapping layers as the wrap is stretched tightly around the load. The tension in the film causes it to cling to itself, creating a strong, cohesive hold without adhesives. This prevents shifting, protects against dust and moisture, and enhances the integrity of the stacked goods. Some films include pre-stretched or reinforced layers for additional strength. Pallet wrap works best when applied with proper tension and coverage, ensuring that the load remains stable during transport and storage while minimizing material waste.
The standard size of pallet wrap depends on the application and whether it is applied manually or by machine. Hand stretch wrap typically comes in widths ranging from 12 to 18 inches, while machine stretch film is usually 20 to 80 inches wide. The thickness (gauge) of the wrap varies based on load requirements, with common options including 60-gauge for light loads, 80-gauge for general shipping, and 100+ gauge for heavy or irregularly shaped pallets. The length of the rolls can range from 1,000 to 5,000 feet, with longer rolls intended for high-volume applications. Pre-stretched film is another option, offering reduced labor effort and improved efficiency. Choosing the right pallet wrap size depends on the weight, shape, and fragility of the goods being transported. Ensuring the correct width and thickness helps optimize cost, protection, and ease of use.

My name is James Thompson, and I’m the editor of this website dedicated to Stretch Film, Pallet Wrap, and Stretch Wrap products.
My passion for packaging began when I noticed the challenges companies face in securing their products efficiently for transportation and storage. This inspired me to delve deep into the world of stretch films and pallet wraps, exploring the latest technologies and best practices.
I aim to provide valuable insights, practical tips, and up-to-date industry trends to assist you in making informed decisions. Whether you’re a small business owner or part of a large corporation, my goal is to support you in optimizing your operations and ensuring your products reach their destination safely.
Thank you for visiting, and I look forward to accompanying you on your journey toward better packaging solutions.
Comments are closed